Smart medical is an idea. It is the product of the latest development stage of medical informatization, the result of the deep integration of 5G, cloud computing, big data, AR/VR, artificial intelligence and other technologies with the medical industry, and the evolution of Internet medical care.
1. What is smart medical?

A study by the National Academy of Medicine in the United States found that 5 percent of outpatient diagnoses were wrong, and 10 percent of those patients died as a result. This represents five deaths due to a wrong diagnosis for every 1,000 patients treated. According to a survey, 20 percent of orthopedic surgeons say they have had wrong-site Surgery in the operating room at least once in their careers. Finally, 210 billion; Statistics show that 210 billion dollars is wasted on unnecessary medical care in the United States.
It may be hard to believe, but those numbers are why the medical-tech industry is growing, projected to grow 15.8 percent (nearly three times faster than the industry as a whole) to reach $390.7 billion by 2024. Among them, not only the traditional medical industry investment, but also Apple, Google, Amazon and other large technology is actively entering the industry. Spurred on by the pneumonia outbreak, Line recently announced that it will launch telemedicine in Japan to reduce the daily burden on hospitals and reduce unnecessary medical services.
In the future, the healthcare industry will continue to introduce more digital technologies to reduce costs while improving outcomes, and the healthcare system will transform dramatically around the patient to dramatically improve the patient experience. What technologies will be brought into the value chain, and how will these technologies solve the current problems of healthcare? In this insight, we will address each of these dimensions.
What is smart medicine?
Smart healthcare is defined as a trend to introduce technologies such as the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and advanced analytics into existing medical processes. These technologies have a wide range of applications in smart medicine, It will further drive technologies such as Teleme Eme Icing, Remote Patient Monitoring, integrated electronic medical record management systems, patient wearables, online medical consultation and appointment booking, or AI visits to the market.
If implemented effectively, these digital technologies can address chronic problems in the healthcare industry, such as lack of medical talent, diagnostic error rates, resource utilization rates, and patient care quality and experience.
However, it’s not just medical procedures that are transforming the Healthcare industry as it goes Smart. Smart Healthcare is about putting the consumer at the heart, building an entire ecosystem, A de-intermediated yet resource-sharing ecosystem of facilities including SHC, smart hospitals, clinics, laboratory crocodile imaging centers, homes, and care centers.
Nowadays, people prefer to manage their health rather than treat them. This is why Smart Healthcare communities have emerged. Although communities like Healthcare have always existed, it is only recently that people’s health awareness has improved and technology has developed. In particular, the Internet of Things and Life style wearable will allow the so-called SHC to take off.
Built on SHC, wearable devices, and the entire smart healthcare ecosystem, in the future, customers will interact with the entire healthcare system all the time. Before seeing patients, they may monitor their health through data on wearable devices, or take regular health check-ups at relevant centers. When there is alarm, patients can search for relevant information through the platform or the resources of the community. At the same time, patients can make an appointment with the hospital through ai-driven programs, which not only accelerates the appointment process. The program will use data analysis to better meet patient needs and reduce wasted resources on the hospital side because of accurate appointments.
During the visit, the hospital can use the data provided by the patient (wearable device data, clinic records, medical examination reports, etc.) to report in advance so that the doctor can provide more accurate diagnosis content. Once a diagnosis is made, doctors and patients can use telemedicine-related solutions to keep track of their illnesses.
2. The history of smart medical

Origin – the birth of medical information system
The story begins with medical information.
In the 1870s, with the rapid development of computer technology, the embryonic form of hospital information system was born in China. In 1978, The General Hospital of Nanjing Military Area Command was the first to introduce domestic DJS-130 minicomputers and began to explore their application in drug management, which was the earliest attempt of computer in hospital management information in China.
In the initial stage, the system is used by single machine and single user, and the information of the whole department is stored in one machine, so the information cannot be transmitted between individuals and departments. Only a few large general hospitals and teaching hospitals have information systems, some of which have developed some small software. At that time, the information system only contains some management modules, such as salary software, outpatient charges, inpatient cost management, drug storage management, etc.
In the decade from 1980 to 1990, with the rise of network technology, some hospitals began to establish small local area networks and independently developed small network management systems based on department management, such as inpatient management, pharmacy management, outpatient pricing and charging drug delivery system.
Since 1990, some hospitals have tried to develop their own Hospital Management System, focusing on medical Information, economic accounting and materials throughout the whole System.
Outbreak — Golden Age of medical information system
From 2000 to 2010, the functions of hospital information systems have been gradually improved and enriched. More than ten subsystems have been derived from the basic subsystems of outpatient management, inpatient management and pharmacy management.
In 2010, HIS started a construction boom. Up to now, the penetration rate of HIS system has reached a relatively high level. Level-iii hospitals have basically reached HIS full coverage, and level-II and below hospitals have basically reached 80% coverage. The traditional HIS system is in a new cycle of upgrading and upgrading. The penetration rate of outpatient and emergency pricing system has reached 80.4%, and the penetration rate of inpatient pharmacy management system, drug storehouse management system, outpatient and emergency ward management system, outpatient and emergency registration system and medical record management system has exceeded 70%.
The Clinical Information System (CIS) is developed at the same time with the construction of hospital Information System. Clinical information system can support the clinical activities of hospital medical staff, collect and process the clinical medical information of patients, enrich and accumulate clinical medical knowledge, and provide clinical consultation, auxiliary diagnosis and treatment, auxiliary clinical decision-making, improve the work efficiency of medical staff, and provide more, faster and better services for patients.
Similar to hospital management System, Clinical Information System also contains many subsystems, such as Laboratory Information System (LIS), Radiology Information System (RIS), Electronic Medical Record (EMR), PACS system (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems), etc.
Smart medical care is the informatization construction and its core is the electronic medical records. On the basis of electronic medical records, it helps medical staff to make primary medical decision support through technical means.
The core of smart management is to carry out fine management for hospitals. Fine management is a very important fine cost accounting. This needs to use the hospital management system for real-time monitoring, and real-time control of the operation of the whole hospital. The earliest hospital management system is HIS system. At present, the hospital management system has been developed very maturely, covering many functional modules, including equipment management, material management, drug management and so on.
3. How does smart Medical work?

Smart medical solutions mainly include two categories: front service system and logistics service system.
For attendance service mainly refers to the business that medical institutions carry out for patients, the public and their own offices.
Smart medical front attendance business module
• Clinical healthcare business system
• Clinical mobile information system
• Regional healthcare collaboration systems
• External interface of hospital integrated management system
Logistics services mainly refer to the support services provided by medical institutions for the management of medical parks.
Logistics business module of intelligent medical treatment
• Public Safety
• Equipment Room Engineering
• ITAS for information applications
• Information Facilities
4. How safe is smart medical? (What are the risks?)

At present, communication, consultation, smart medical equipment applications, mobile payment are mostly based on mobile terminals. The business of emerging Internet medical manufacturers mainly relies on APP, so ensuring the security of APP is also a top priority.
In recent years, the emergence of smart medical treatment has slowly begun to change traditional medical treatment. Many Internet companies have emerged in the market to enter the medical industry in subdivided fields. Internet medical companies that are relatively well-known to the public provide routine services such as online consultation, appointments, health advice and patient communication. Some intelligent hardware manufacturers also aim at the medical market and launch intelligent and home-oriented medical equipment, similar to household blood pressure meter and urine test meter, which provides the possibility of home testing through associated APP and can monitor health data in real time. Through access to mobile Internet, some hospitals enable patients to register, see a doctor, take medicine, and pay through mobile terminals, optimizing the payment process and saving a lot of manpower.
At present, these exchanges and consultations, smart medical equipment applications, mobile payments are mostly based on mobile terminals. The business of emerging Internet medical manufacturers mainly relies on APP, so ensuring the security of APP is also a top priority. The author suggests that relevant enterprises in the medical industry can create more secure APP applications by avoiding risks when constructing mobile businesses.
Information disclosure
While new services such as mobile medical services provide users with services, users’ personal information is also facing more and more potential risks. Due to the Internet application exposed security vulnerabilities caused by the user name, address, phone, ID number, consumption records, inspection reports and other important personal information leakage problems occur from time to time.
Application of piracy
In general, pirated apps include: inserting/replacing AD SDKS to earn AD revenue; Modifying payment channels to intercept developer income; Inserting virus/Trojan horse to steal user information; Modifying pictures to insert ads, obtaining advertising revenue, etc. It seriously infringes on the interests of hospitals, developers and users.
APP to crack
After cracking the hospital/medical APP, hackers can use code tampering to attack by bypassing the original authentication process. The target includes attacking registration, payment and other links, so that patients cannot register and pay normally.
Malicious viruses and AD placement
Cracked the original hospital/medical mobile APP, implanted malicious programs, enticed users to download through WIFI, TWO-DIMENSIONAL code, forum, application market and other ways, installed and run programs without users’ knowledge or authorization, resulting in malicious fee deduction, information theft, spread of spam, fraud and other illegal activities.
5. Advantages and benefits of smart medicine
Smart medicine is a patient-data-centered medical service model, which is mainly divided into three stages: data acquisition, knowledge discovery and remote service. Compared with traditional medicine, smart medicine has the following advantages:
1. Use a variety of sensor devices and medical instruments suitable for home use to automatically or self-collect all kinds of vital signs data of human body, so as to reduce the burden of medical staff and obtain more abundant data.
2. Medical staff can provide telemedicine services using data automatically collected and transmitted to hospital data centers via wireless networks, thereby improving service efficiency, alleviating queuing problems and reducing transportation costs.
3, wisdom, health care system can be centralized management, the data collected using widely Shared and depth of the data, help to solve the key cases and incurable diseases, can at a lower cost for healthy people, the elderly and patients with chronic diseases to provide long-term service, fast and stable health monitoring and diagnosis and treatment, reduce the risk, Indirectly reducing the demand for scarce medical resources such as beds and blood plasma.
4. Information health systems for smart Medicine allow patients and doctors to have access to all the necessary information about an individual’s health status whenever they need it, helping healthcare professionals focus more energy and time on providing medical care and care.
6. Application examples of smart medical

Ai-assisted diagnosis and treatment
In the traditional medical system, doctors make diagnoses based on personal expertise and experience. Now, thanks to AI technology, doctors can get ai-assisted diagnosis results.
Image film, including X-ray, ultrasound and CT, can be analyzed with the help of AI, helping to improve film reading efficiency and diagnostic accuracy.
Drug administration
Traditional drug management and distribution rely on healthcare workers.
With the help of drug management system, we can track the storage and transportation process of drugs and trace the source of drugs. With the help of robots, drugs can be quickly sorted.
AI can be used to help judge whether the prescription is reasonable, whether the dose is accurate, and whether there are risks of contraindications and allergies.
Equipment management
All medical devices are connected to the hospital system through the Internet of things technology. The hospital can query the relevant data, service life and fault information of the device.
When medical supplies are insufficient, they can also be monitored through the Internet of Things system for timely reminder replenishment.
With the help of some AI unmanned disinfection equipment, rapid disinfection of medical instruments can be realized, the efficiency of the use of instruments can be improved, and the waiting time of patients can be reduced.
Remote monitoring
By wearing wearable devices for inpatients and connecting ward monitoring facilities, nurses can remotely monitor patients’ vital signs and the environment of the ward.
By installing electronic fences, patients can be prevented from leaving the ward without permission. Through electronic access control and camera, you can prevent irrelevant people from entering the ward.
Mobile ward-round
Now, more and more hospitals are turning up mobile trailers.
When doctors make rounds, they push the mobile car, which is wirelessly connected to the hospital system to access and record patients’ electronic medical records. In special cases, doctors can also make remote ward rounds.
Electronic wristband
By wearing an electronic wristband, patients can complete patient identification throughout the hospital stay. Such as dispensing medicine, transfusion, ward rounds, payment, operation, first aid, etc.
If necessary, facial recognition can also be used to verify the patient’s identity before medication.
Telemedicine
A large number of telemedicine scenarios are introduced when the hardware and software capabilities of the hospital are insufficient to complete the treatment. For example, remote consultation, remote examination (B ultrasound, etc.), remote pathological section analysis, remote teaching, remote surgery, etc.
Remote surgery
It refers to surgeons performing operations on remote patients in real time in different places with the help of robotics based on 5G, OTN and other high-performance networks.
Because surgery is an invasive operation, human organs are fragile and close together, and a slight mistake can lead to serious consequences, even life-threatening. So, remote surgery is very risky, very demanding, more difficult than remote driving.
To successfully implement remote surgery, the transmitted image must be clear enough, the transmitted signal must be stable enough, the signal delay must be low, the packet loss rate must be low, and the reliability must be high.
Traditional 4G and wi-fi wireless communication technology, can not meet the requirements. 5G, with its features of high speed, large bandwidth and low latency, can meet the requirements in principle.
In the process of remote surgery, data is collected by multiple ultra-high-definition cameras with 4K or more, and transmitted back through 5G network. The remote operator performs the operation from the console, based on images. The operating platform will collect and remotely transmit the operation actions to the surgical site, and the on-site mechanical arm will complete the operation.
It is worth mentioning that combined with VR/AR technology, doctors will get a better surgical experience. VR/AR technology is also widely used in remote teaching (training).
5G ambulance
Finally, we will mention a special out-of-hospital intelligent medical scene, which is a 5G emergency vehicle.
With the help of 5G technology, emergency vehicles can send vital signs data of patients to the hospital quickly, making it easier for hospital medical staff to prepare in advance. Hospital staff can also remotely direct ambulance staff to carry out necessary rescue work.
Because of the high speed of the ambulance, it is very difficult to send back a large amount of data. Traditional 4G is very difficult, and Wi-Fi and satellite are impossible.
The above are the existing scenarios and applications related to smart medical care.
8. What is the cost of smart medical?

Many times we go to the hospital and are instructed by the medical staff to sign this or do that, before which we often know very little about the services and fees. In the United States, companies are already experimenting with smart medical technology to help employees reduce the number and size of their medical needs.
According to a Survey by PolicyGenius, only 4 percent of Americans understand the various insurance items correctly and know exactly how much they should pay for their medical care. The arrival of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data and robotics will deal with these problems for them.
Prescription drugs are another virgin territory reserved for smart medical technology. The annual cost of prescription drugs will typically account for about 15 to 25 percent of your annual health insurance cost. What’s so maddening is that prescription drug prices vary from plan to plan, and your doctor doesn’t even know what she’s charging you. Smart medical technology can make it easier to solve these problems, as well as the plethora of prescription lists, treatment alternatives, generics, discounts, drug prices, bulk drugs, mail-order services, and more. And provide us with more affordable recommendations so that we can save more money.
The cost of the same medical program can be 133% higher in the same city. There may be times when you want to know about a medical service, but sadly the answer is “don’t know, don’t know”. You will not be told the price until you have accepted the service. But through smart medicine, these questions will be presented to us one by one, and no matter what questions we ask, we can get the most reliable answer in the shortest time.
Although there are still many technical bottlenecks in the development of smart medical treatment at the present stage, and many obstacles will be encountered, the future potential is infinite. It is believed that smart medical treatment in the future will greatly improve the efficiency of the entire medical system, so that more people who need medical services can really benefit.
9. What devices are needed for intelligent medical treatment

As the key to collecting data, sensors play an important role not only in industrial and electronic devices but also in the medical industry. Various physical is made into equipment to collect various physiological indicators of the human body in the medical field.
Sensor application in the medical industry is very broad and vital, its application can greatly improve the safety of medical equipment, reliability, and stability, and in the medical device industry, mainly involved in pressure, flow, temperature and humidity, infrared, oxygen sensors, such as common applications are breathing apparatus, anesthesia apparatus and instruments, diagnostic monitoring instruments, etc.
Infrared thermopile sensor
The thermopile sensor is the core component of the temperature gun, which has the characteristics of high cost performance, long service life, fast response speed and high accuracy. The NTC chip helps infrared thermopiles get more accurate measurement data in temperature monitoring.
Mainly used for: non-contact temperature measurement; Infrared temperature non-contact measurement of ear temperature, forehead temperature; And household appliances (microwave oven, hair dryer, air conditioning, etc.) temperature measurement and control; Human presence detection;
MEMS flow sensor
The flow sensor can measure or adjust the flow velocity of the gas or liquid in the tube. It has the characteristics of high precision, fast response, good repeatability and accurate measurement of minimal flow.
Mainly used in intensive care ventilators, portable ventilators, portable instruments, air and environmental protection, industrial process control, etc.
MEMS pressure sensor
Pressure sensors play an important role in medical patient history examination and minimally invasive surgery monitoring, arterial blood pressure, intracranial pressure, pulmonary pressure and other important parameters in the medical process. In addition, medical care needs monitoring, treatment, health care, etc., and are inseparable from the precise measurement of pressure sensors.
In addition to sophisticated medical and surgical facilities, electronic sphygmomanometers and other medical supplies in daily life are also used to achieve autonomous real-time measurements through pressure sensors.
Ozone sensor
The advanced oxidation process with ozone as its core can effectively inactivate viruses, and finally decompose ozone into oxygen.
Ozone is often used in the medical field such as operating rooms, disposal rooms, infectious disease areas, burn wards, waiting areas, hospital toilets and other areas of disinfection and purification. (And ozone allowance monitoring in space after elimination ~)
MEMS breath sensor
About 80 to 90 percent of bad breath is linked to oral disease, and it comes directly from bacteria in the mouth that break down food waste and produce volatile sulfides (VSCs) — the main components of bad breath.
The causes of bad breath are complex, but the main culprit is usually hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas. Through the detection of bad breath, the patient may have related diseases.
Flexible pressure transducer
The flexible pressure sensor is based on a new nano pressure-sensitive material with a comfortable young’s modulus of ultra-thin film substrate one-time patch.
The resistance value of the sensor changes when the external pressure is sensed. After sensing the pressure change, the simple circuit can make the sensor change the pressure signal into the electrical signal output of the corresponding change intensity. Mainly used in intelligent breathing belts, intelligent anti-snoring pillows, intelligent insoles, intelligent gloves, and intelligent helmets.
10. What is smart medical software?

DrChrono
DrChrono EMR is available on phones, desktops, Apple Watch, and tablets, enabling providers to make updates without having to connect to a workstation.
Workflow, patient engagement, and scheduling are composed of the system to prevent providers from having to learn multiple interfaces.
Kareo
Kareo provides cloud-based electronic health record solutions for healthcare practices. The Kareo EHR is qualified to help medical practices obtain meaningful proof of use. The appeal is affordability, practicality and mobility. The Kareo EHR includes dynamic patient, documentation, and drug management capabilities.
AdvancedMD
AdvancedMD is the leading software solution for private practice. Medical billing, Fully integrated EHR, and patient experience tools help you run your entire practice from a single cloud-based platform. Say goodbye to cross-system comparisons and data differences.
CareCloud
CareCloud provides cloud-based services and software for the healthcare industry. They help practices improve patient care quality while maximizing profitability by offering EHR, and revenue cycles. CareCloud provides solutions for hospitals and small and large clinics in a variety of specialties.
Cerner
Cerner provides EHR solutions for a variety of medical practices. Cerner’s dynamic EHR is ideal for professional practices, urgent care centers, and group medical clinics. While improving efficiency and reducing errors, the program ensures compliance with HIPAA regulations. A convenient “chart search, a user-friendly dashboard, and secure access to records are some of the key features of the program.
Epic
Epic’s EpicCare dynamic EMR platform is ideal for multi-site practices. An intuitive “smart software” feature is included in this EMR solution to suggest corrections. Epic’s EMR solution is ideal for hospital systems seeking an intuitive, secure and efficient approach to electronic medical records management.
WebPT
With WebPT, therapists and front desk staff can access a patient’s medical records from any device in the support network. WebPT provides a foreground package that includes the tools needed to run an organized clinic.
NextGen
By helping users coordinate patient care while meeting healthcare reform requirements, NextGen® EHR solutions meet the needs of outpatient practices of all sizes. NextGen® Enterprise EHR provides a scalable and fully integrated system that helps customers achieve patient engagement, interoperability, value-based care delivery, and regulatory compliance.
Practice Fusion
Practice Fusion’s full-featured EHR is free due to advertising support, although a premium version can be purchased to remove ads. Testing, and referral management, charting, electronic prescribing, scheduling, and billing are part of Practice Fusion’s integrated platform.
11. What is the market for smart medical?
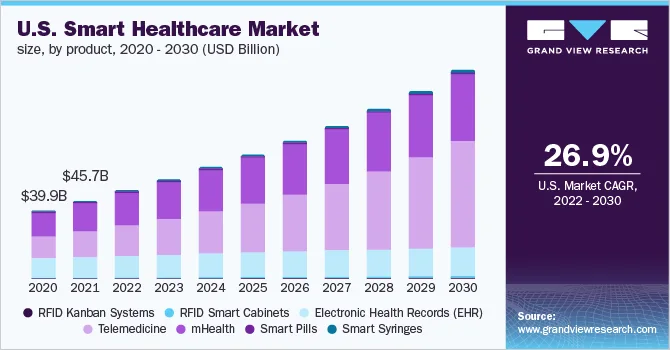
The global smart healthcare market is estimated to be worth $153.6 billion by 2021 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.3% from 2022 to 2030. Digitization has transformed the healthcare industry. Adoption of mHealth has increased dramatically over the past few years.
There has been a sudden increase in demand for smart healthcare products with the emergence of COVID-19. The adoption rate of smart healthcare increased during the pandemic and is anticipated to grow further in the post-COVID-19 context. Hence, many businesses are expanding their services or products; For instance, Vera Smart Health invested approximately $20 billion to expand its services to include drug delivery, drug delivery, in-home testing and diagnostics, and drug delivery in November 2020.
The growing participation of industry participants is expected to further drive the smart healthcare market. For instance, Phillips launched a new app for acuity-based scoring tools for care managers in April 2020. And Teladoc Health launched Teladoc Medical Professionals for patients with complex physical health conditions in October 2019.
In addition, in March 2020, the NHS in the UK encouraged front-line healthcare facilities to use telemedicine to reduce the spread of COVID-19. As of now, nearly 340 million medical consultations are recorded in primary care clinics in the UK each year, of which only 1% are conducted via video calls.
In 2021, North America dominates the smart healthcare market with a revenue share of more than 33.0%. This is due to supportive government policies on digital health deployment and the accessibility of a digitally literate infrastructure. Moreover, the presence of major market players, increasing awareness of connected healthcare, the use of health-related applications, and high penetration of the Internet and smartphones are some of the essential factors driving the growth of the smart healthcare market.
The AMA said that nearly 76% of hospitals in the United States use telemedicine to connect with consulting practitioners and patients because of its higher healthcare value and affordability.
India, Australia, and Japan show great potential due to their increasing investment in smart healthcare. Companies are increasingly investing in telemedicine services as COVID-19 cases increase in the region. On 14 April 2020, Huawei was praised for providing wireless networks, conferencing, and smartphones in Thailand, Bangladesh and Malaysia.
















